This incidence at Kolkata has raised questions regarding the safety of patients in hospitals. Death of 89 victims in the tragedy has initiated discussions concerning the safety measures adopted while building the hospitals. Police officials have noted it as an incidence of homicide and negligence.
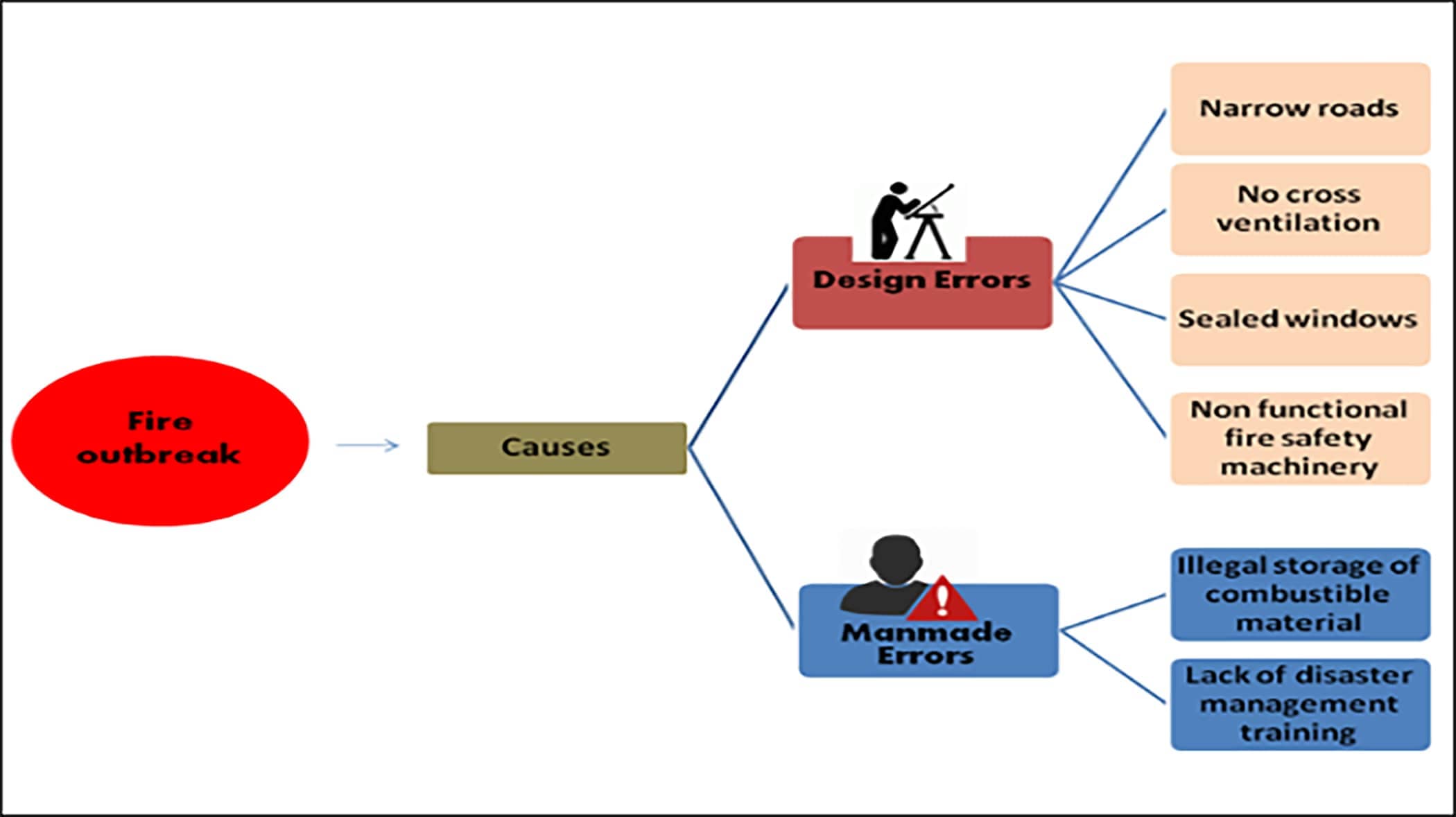
The fire broke out at wee hours of December 2011, around 3 am at AMRI hospital when the majority of the 160 patients were asleep. This was a privately-run, five-story facility situated in an area which was connected by narrow roads. This created difficulty in rushing ambulances and fire brigade trucks near the hospital. Fire brigade officials mentioned that building structure caused difficulty in bringing big hydraulic ladders near the hospital to evacuate the patients trapped inside.
According to reports, the fire had originated in the electrical department in the basement. It is estimated that an electrical short circuit in the basement was the cause of the fire. This area was used as an illegal store for combustible material like LPG cylinders, engine oil, PVC pipes, bedding, etc which caused the spread of fire. Flames of the basement fire spread up through the floors and smoke leaked into the building through air conditioning and ventilation shafts. The fire fighters had a hard time to rescue victims of the fourth and fifth floor by breaking the glass window panes of sealed air-conditioned floors which were devoid of fire escapes.
It was noted that fire protection mechanisms installed inside the hospital were incapable to stop the spread of fire. The patients were alerted by screams and smoke instead of a fire alarm. The sprinklers were not in working condition. The mechanism for cross ventilation was absent which turned the hospital into the gas chamber. Grief-stricken relatives of the victim patients have complained that the hospital staff had locked from inside to prevent people from fleeing which increased the death toll due to suffocation. It was feared that radiation leak occurred after the fire damaged its radiology and oncology department which worsened the situation.
Fire created wreckage in the hospital system as large numbers of patients admitted were not in a better condition to be evacuated within a short period of time. The significant aspect in such cases is to realize the necessity of developing strategies for fire prevention along with adoption of disaster management remedies in case of fire outbreak which was nonexistent in this case. The fire caused irreparable damage to both patients and hospital. Loss of lives destroyed patients trust. The license of the hospital was canceled immediately after the tragedy. Loss of infrastructure and equipment posed financial losses.
Owing to this incidence it is essential to design the set up such that it considers associated fire risks. Equipment must be maintained with respect to the adherence of safety standards. Parking and roads within the hospitals must follow fire safety measures. Many hospitals ignore such safety issues due to financial constraints or improper guidance. It is important that hospitals must realize that intelligent designs to ensure fire safety by adopting standard guidelines which are possible within the financial constraints. Hospital management must seek guidance with respect to designing and maintaining the safety of the entire system. Awareness regarding such safety practices will enable healthcare sector to curb irreparable losses associated with fire outbreak. Hospitals are places where patients are cured of their ailments, therefore, it is essential to maintain the safety and functionality of such structures. This ensures responsible healthcare system with patients’ safety as the prime concern.
In order to overcome this burden of responsible and safe healthcare system, Techniche Imunita offers assistance. We help you ease the load of hospital management and ensure safe functioning of the hospital by following standard guidelines and regulation within the financial constraints of the hospitals.